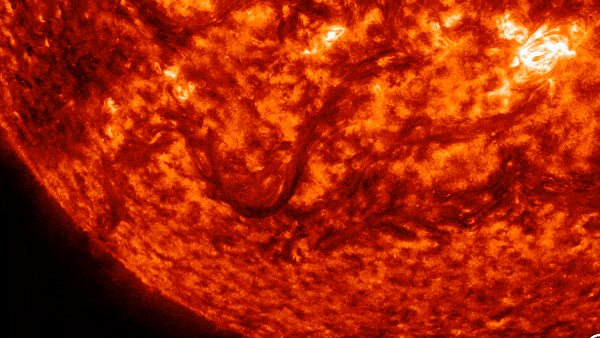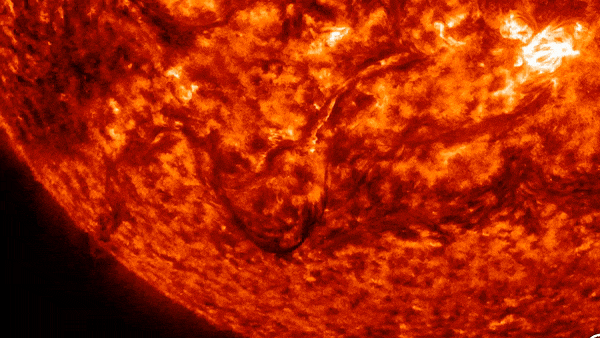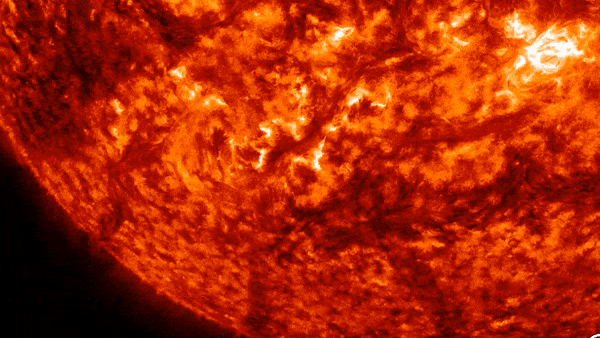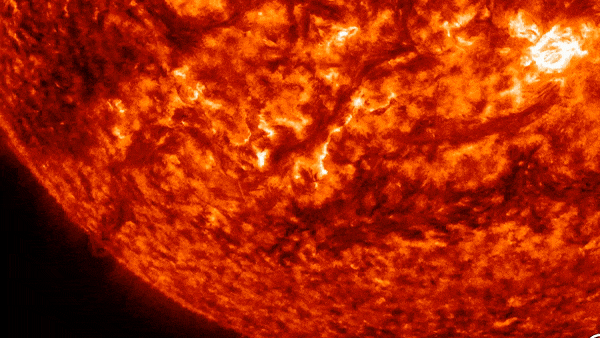
A vast “valley of fire” at least twice the width of the United States was carved into the sun’s southern hemisphere on Wednesday (October 31).
The culprit? Large magnetic filaments explode from sunAccording to spaceweather.com. This activity created a valley about 6,200 miles (10,000 km) wide and 10 times as long.
These solar filaments are enormous arcs of electrified gas, or plasma, that are suspended above the surface of the Sun. They’re sneaking through Sun atmosphere, in response to our star’s magnetic field. When the magnetic field becomes unstable, the string collapses, which can lead to spectacular explosions — like the one seen in the video above.
Related: For example, solar maximum will arrive sooner and last longer than previously expected
“Notice how it starts moving very slowly and gradually accelerates until it becomes unstable and erupts,” said solar physicist Keith Strong Written on X (formerly known as Twitter), after the volcanic eruption.
Scientists did not determine whether the eruption led to or not Coronal mass ejection (CME) – where charged plasma is released from the Sun’s upper atmosphere, the corona, into space. Data from NASA Solar and heliospheric observatory (SOHO) Coronographs will reveal whether that is soon Land He is in the line of fire.

If at least part of the coronal ejection was directed toward Earth, the strong currents would be magnetized Solar wind It can impress twilight Later this week. (The aurora borealis is also known as the aurora borealis or northern lights in the Northern Hemisphere and the aurora australis or southern lights in the Southern Hemisphere.)
Auroras are caused by energetic particles from the Sun colliding with the Earth’s upper atmosphere at speeds of up to 45 million mph (72 million km/h). Earth’s magnetic field It then redirects the molecules towards the north and south poles.
The electrically charged particles then enter the Earth’s atmosphere, Excitation of gas atoms and molecules And generating twilight. The process is similar to how neon lights work: when molecules and Atoms Get “excited” by ElectronsThey must return to their original energy (ground state) and do so by releasing energy in the form of photons (light). The color of the neon light depends on the mixture of gases inside the tube, just as the color of the aurora borealis depends on the mixture of gases in the atmosphere.
The current aurora season has already put on some dramatic displays and experts predict it will continue to intensify as we approach “solar maximum” – the peak of solar activity in nearly 11 years. Solar cycle.

“Web maven. Infuriatingly humble beer geek. Bacon fanatic. Typical creator. Music expert.”





More Stories
SpaceX launches 23 Starlink satellites from Florida (video and photos)
A new 3D map reveals strange, glowing filaments surrounding the supernova
Astronomers are waiting for the zombie star to rise again