
The space agency said on Channel
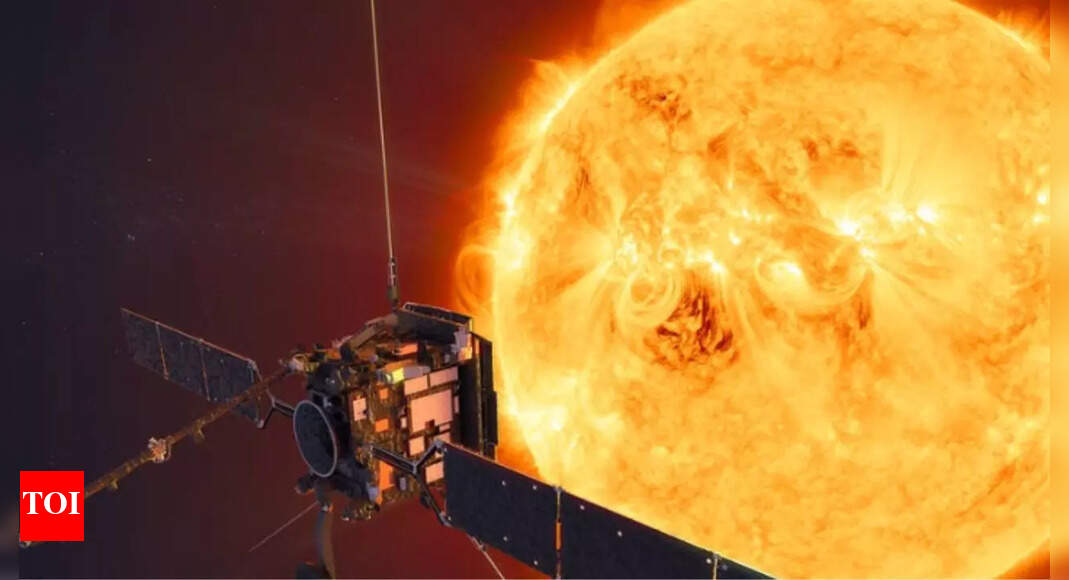
Isro’s Aditya-L1 mission, launched on September 2, 2023, is India’s first mission dedicated to studying the Sun, specifically the photosphere, chromosphere and corona. It has 7 distinct payloads developed, all developed indigenously. Five by Isro and two by academic institutes in collaboration with the space agency.
Aditya-L1 will operate in a “halo orbit” around the L1 point between the Sun and Earth, which is located about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth, which is about 1% of the Earth-Sun distance.
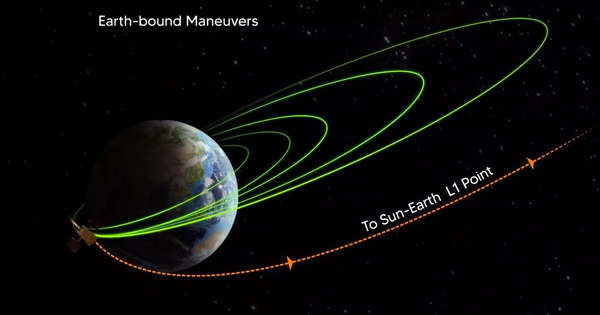
Lagrange points, also known as gravitational points, are unique locations in space where the gravitational force of two massive bodies (such as the Sun and Earth) precisely equals the centripetal force required for a small body (such as a spacecraft) to move with them. This makes Lagrange points an excellent location for spacecraft where orbit corrections and thus the fuel requirements needed to maintain the desired orbit are kept to a minimum.
The Aditya-L1 mission has four main scientific objectives:
- Understanding coronal heating and solar wind acceleration
- Understanding coronal mass ejections, flares, and near-Earth space weather
- To understand the coupling and dynamics of the solar atmosphere
- Understand the distribution of solar wind and temperature variation

“Web maven. Infuriatingly humble beer geek. Bacon fanatic. Typical creator. Music expert.”





More Stories
SpaceX launches 23 Starlink satellites from Florida (video and photos)
A new 3D map reveals strange, glowing filaments surrounding the supernova
Astronomers are waiting for the zombie star to rise again